Do you ever think about the environmental impact of your morning coffee? The journey of coffee from farm to cup involves various stages that contribute to its carbon footprint.
The carbon footprint of a single cup of coffee can range from 50 to 150 grams of CO₂, depending on the farming, processing, packaging, and brewing methods used. Understand the carbon footprint of coffee1
Coffee, while beloved, comes with environmental implications. Let’s uncover the details.
What is the environmental footprint of a cup of coffee?
The environmental footprint of coffee goes beyond just carbon emissions—it includes water usage, land degradation, and biodiversity loss.
A cup of coffee impacts the environment through farming, deforestation, transportation, energy-intensive processing, and brewing practices. Learn about coffee's environmental impact2
Understanding the full footprint of coffee requires tracing its lifecycle from seed to sip.

Dive Deeper: The lifecycle stages of coffee production
1. Cultivation and Farming
Coffee farming often involves deforestation to make way for plantations, leading to loss of biodiversity. Additionally:
- Fertilizers and pesticides: These chemicals release nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas. Explore sustainable fertilizer practices3
- Irrigation: Growing coffee consumes significant amounts of water, especially in arid regions. Discover water-efficient coffee farming4
2. Harvesting and Processing
Post-harvest processing includes:
- Washed process (wet method): Requires large amounts of water and generates wastewater.
- Natural process (dry method): Less water-intensive but can result in higher methane emissions if waste is not managed properly. Compare coffee processing methods5
3. Transportation
Coffee is a globally traded commodity, with beans traveling thousands of kilometers from producer countries to consumers. Transport emissions contribute significantly to its footprint.
4. Brewing
Brewing at home or in cafes also adds to the footprint, depending on:
- The type of coffee machine used.
- Energy sources powering the brewing process. Read about energy-efficient coffee brewing6
Additional impacts:
Coffee packaging, often made of non-recyclable materials, adds to environmental waste. Single-use coffee pods are especially problematic. Explore sustainable coffee packaging options7
Why is the carbon footprint of coffee so high?
Coffee’s high carbon footprint stems from its resource-intensive production and global supply chain.
Deforestation, energy-intensive processing, long transportation distances, and inefficient brewing methods contribute to coffee’s significant environmental impact. Learn more about coffee's carbon footprint8
Let’s delve deeper into these factors.
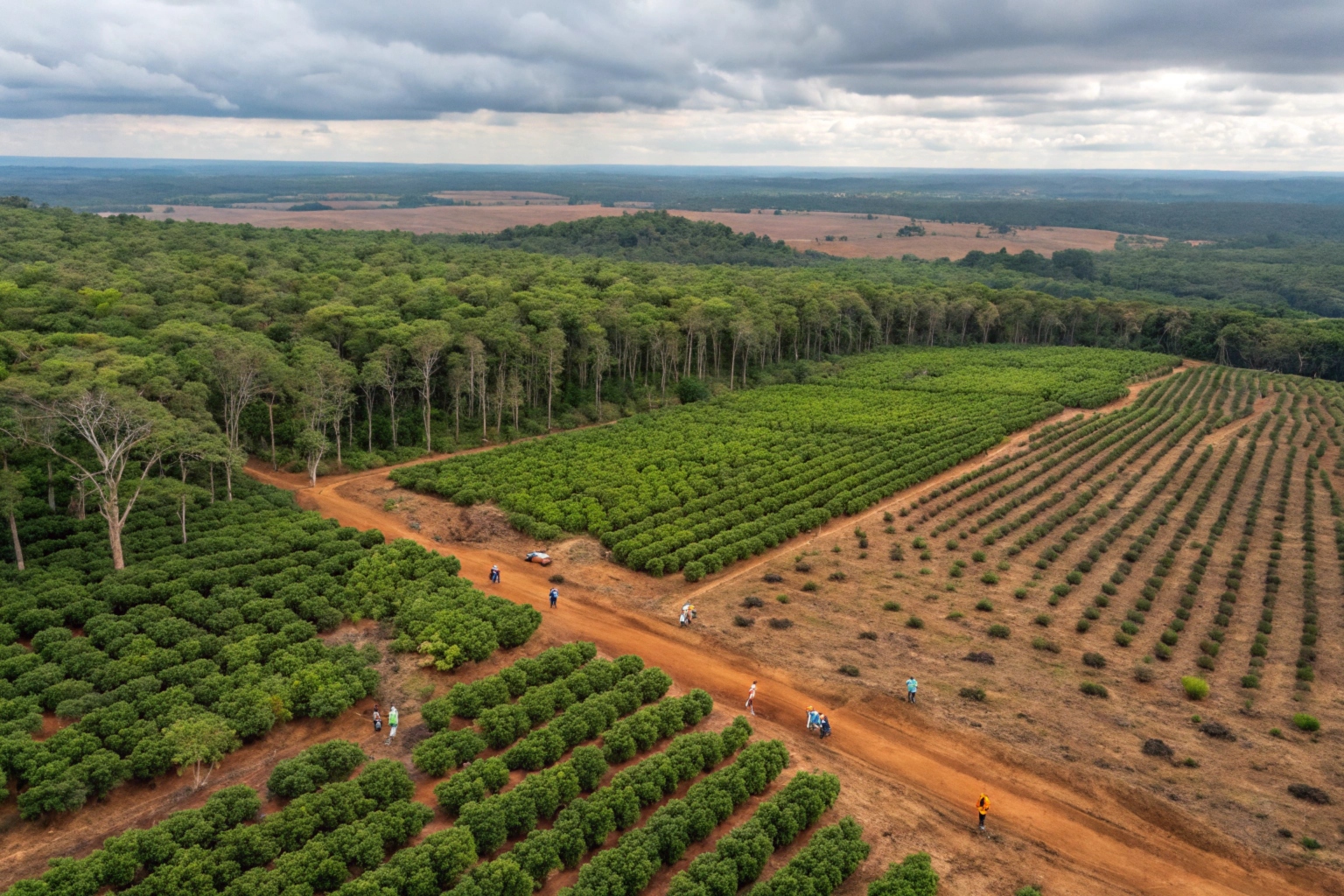

Dive Deeper: Breaking down the major contributors
Deforestation for Coffee Farms
Many coffee plantations replace tropical forests, which are vital for carbon sequestration. For example:
- Brazil and Vietnam, two of the largest coffee producers, have seen significant deforestation linked to coffee farming. Impact of coffee farming on tropical forests9
Fertilizer and Pesticide Use
The production and application of nitrogen-based fertilizers release nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas 300 times more potent than CO₂. Additionally:
- Overuse of fertilizers can lead to soil degradation, reducing carbon storage capacity.
Energy Use in Processing
The drying, milling, and roasting of coffee beans require substantial energy, often derived from fossil fuels. Explore energy-efficient coffee roasting10
Transportation Emissions
Coffee is often shipped by sea or air, covering vast distances. Air-freighting specialty coffee beans increases the carbon footprint substantially.
Waste and Brewing Practices
Brewing methods vary in their energy use:
- Capsule-based machines generate waste and use more energy per cup.
- Traditional drip coffee machines are more efficient but require large amounts of water.
Solutions to reduce the impact:
- Encourage shade-grown coffee farming to reduce deforestation. Read about shade-grown coffee benefits11
- Invest in renewable energy for processing and brewing.
Footnotes:
-
Explanation of the carbon footprint range for coffee production and consumption. ↩
-
Overview of environmental factors influenced by coffee production. ↩
-
Details on using eco-friendly fertilizers to mitigate environmental impact. ↩
-
Insights into water conservation methods in coffee farming. ↩
-
Comparison of wet and dry processing methods in coffee production. ↩
-
Tips on reducing energy usage during coffee brewing. ↩
-
Suggestions for eco-friendly and recyclable coffee packaging. ↩
-
Analysis of deforestation's role in increasing coffee's carbon footprint. ↩
-
The role of tropical deforestation in coffee production's environmental impact. ↩
-
Innovations in energy-saving roasting technology for coffee. ↩
-
Benefits of adopting shade-grown coffee farming practices. ↩